Introduction
The toxic effects of accidental fall of plant juice such as crown flower, corn cockle, Madar and beach apple have been described earlier in ophthalmic literature.1, 2, 3, 4 Of these there have been many reports on Calotropis induced keratitis.5 The latex of the Calotropis sap has been shown to be pro-inflammatory which results in endothelial toxicity causing stromal oedema.6
The effects of orange juice splash into the eye have not been described in literature. We describe one such unusual case where orange rind juice was squeezed into the patient’s eye.
Case Report
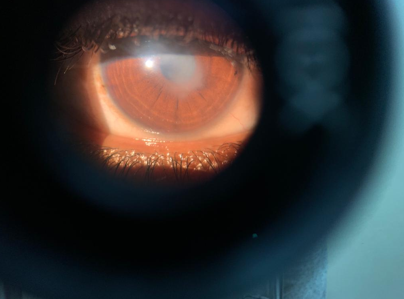
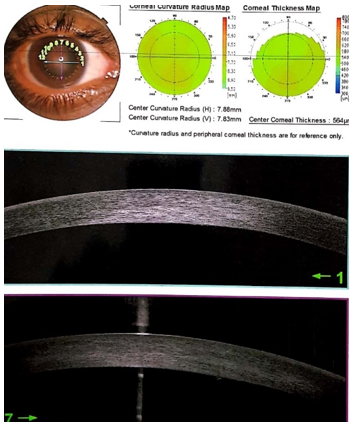
A 21-year-old male presented with complaints of redness, watering and photophobia in right eye, within 24 hours of orange rind juice splash into his right eye. The orange rind juice was directly squeezed into his eye as a prank. Patient did not wash his eye immediately and reported to an ophthalmologist after 24 hours. On examination patient had an uncorrected visual acuity of 6/60, N10 in the right eye which improved to 6/9 with full correction but he continued to complain of haze. Slit lamp examination of right eye revealed mild conjunctival congestion and central corneal stromal oedema of approximately 5mm × 3mm (Figure 1) with an intact overlying epithelium and normal sensations over the affected cornea. Anterior chamber showed no reaction. Rest of the anterior and posterior segment examination were within normal limits. The pH of the right eye was 6. A thorough eye wash was instituted with 1 litre of normal saline and a repeat pH was 7. On fluorescein staining, cornea did not take up any stain showing no epithelial defects. His left eye examination revealed a vision of 6/6, N6 with normal anterior and posterior segments. Anterior segment OCT revealed central stromal oedema with a central corneal thickness (CCT) of 660 µm and oedema was denser in the posterior stroma. Patient was diagnosed with Orange juice induced endothelialitis.
He was started on topical steroid-prednisolone acetate 1% along with lubricating eye drops. After 48 hours patient was examined and examination showed resolving stromal oedema which had reduced to 3×2 mm in size Figure 2. His uncorrected visual acuity was 6/18. AS-OCT revealed resolution of corneal swelling (Figure 3). The corneal thickness had significantly reduced to 564µm, with only posterior stromal oedema. Patient was continued on topical prednisolone acetate 1% on a tapering dose.
Discussion
The toxic effects of accidental fall of plant juice have been described in literature. We did a thorough literature search and could not find any publications on orange rind/ juice induced keratitis. The predominant organic acid in orange juice is citric acid; but other organic acids, namely, tartaric, malic, benzoic, and succinic, have been reported as well, making its pH in the range of 3.3 to 4.66. The chemical composition of orange oil has also been studied and showed to contain alkaloids, saponins, terpenes, resins, flavonoid, phenols, tannins and sugars.7
Orange juice is an irritant to the eye and is known to cause burning sensation if it splashes into the eye and an eye wash has been advised following accidental exposure. In our patient orange rind juice was directly squeezed into his right eye and he probably had an exposure to concentrated juice. The patient did not wash his eyes after it and hence the chemical could have percolated into the cornea causing endothelial damage therefore resulted in corneal oedema.
We recognised the endothelialitis and started the patient on topical steroids and lubricants to which the patient responded. Presence of central stromal oedema warrants a thorough history of any accidental exposure to plant or fruit juices. The ophthalmologist needs to be aware of this finding and investigate it like any chemical injury and check pH. It is also important to recognise the corneal layer which is affected as this determines the treatment. Epithelial defects would require lubricating drops and measures to ensure healing of epithelium while endothelial injury requires steroids to reduce inflammation and facilitate recovery of endothelial function. Endothelialitis responds well to topical steroids and there is a need to recognise this and start the patient immediately on appropriate treatment.
To our knowledge this is the first reported toxic corneal effect of direct contact with orange juice.