- Visibility 378 Views
- Downloads 53 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijooo.2021.030
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Epidemiology, clinical profile, complications and treatment outcomes of chronic dacryocystitis in a tertiary care hospital in post lockdown era: An observational study
- Author Details:
-
Antarlin Ghosal *
-
Pranati Chaudhury
-
Siddharth Kumar
-
Jyotish Khilar
-
Nirupama Rout
Abstract
Aim: to study the epidemiological factors, clinical features, complications and treatment outcomes of chronic dacryocystitis in Odisha after nationwide lockdown in 2020.
Materials and Methods: An observational study was designed from July 2020 to December 2020 in Regional Institute of Ophthalmology, Cuttack, Odisha. Total of 187 patients presenting with chronic dacryocystits were evaluated thoroughly in various epidemiological parameters. The history and clinical features were noted. After proper evaluation and conservative treatment, those patients were subjected for surgery and the surgical outcomes are followed-up upto 3 more months, i.e. March 2021.
Results: The prevalence of chronic dacryocystitis was around 1.224%. Among the 187 patients, 112 were females (59.9%). The disease was found in highest proportion in the age group of 51-60 years (30.5%) followed by 25.7% in the age group of 61-70 years. 90.4% were from rural population. Socioeconomic status and living standard was found to be a significant factor, people belonging to class 4 & 3 were affected more. Majority of the affected were housewives (39.6%) and farmers (21.9%) followed by small businessmen (13.9%) and wage laborers (12.9%). Epiphora was the commonest presenting symptom in 71.6%, followed by mucopurulent discharge in 29.9% and swelling near the medial canthus in 12.3% cases. Complications like conjunctivitis, keratitis, preseptal cellulitis, cutaneous fistula were present in 6.4%, 8.4%, 7.5% and 5.9% cases respectively in our study group. The success rate of external DCR was reported as 85.8% in this study.
Conclusion: Chronic Dacryocystitis, though a common problem of lacrimal drainage system, is much less recognized disease, specially in rural population and in lower socio-economic community in Odisha. Thus patients may present late with one or more complications, e.g. conjunctivitis, keratitis, preseptal cellulitis, lacrimal abscess, mucocele, cutaneous fistula, which is the current scenario in post-lockdown 2020 era. Maintaining all precautions and guidelines for COVID-19, we should not delay treating these patients with surgical measures. The surgical success rate (85.8%) however was not affected much in spite of all these factors.
Introduction
Chronic dacryocystitis is a long standing infection of the lacrimal drainage system, resulting in blockage of the normal drainage system.[1] Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) is the predominant cause of dacryocystitis as obstruction and subsequent retention of tear and mucous leads to secondary infection.[2] The cause of nasolacrimal duct obstruction is idiopathic in most of the cases.[2] However, secondary obstruction may be caused due to trauma, chronic sinusitis, tumour, granulomatous diseases (Tuberculosis, Wegener’s Granulomatosis).[3] Chronic dacryocystitis leads to continuous epiphora which is the most common presenting feature. Other symptoms may be mucoid, muco-purulent or purulent discharge, pain, swelling of lacrimal sac area, chronic conjunctivitis or keratitis, pre-septal cellulitis etc.
External Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is the treatment of choice for most patients in idiopathic acquired NLDO. It is a surgical procedure in which an anastomotic pathway is created between the lacrimal sac and the nasal mucosa through a bony ostium.[4] Dacryocystectomy (DCY/DCT) is done in old ages with comorbidities or in presence of any pathology in the nasal mucosa or bony structures.[4] Secondary NLDO is managed according to the causative pathology.
Though chronic dacryocystits due to NLDO is idiopathic mostly, there are few social and demographic factors which influence its occurrence, as stated by previous few studies. Moreover, the effect of COVID-19 pandemic and the prolonged nationwide lockdown (2020) has influenced everyone’s lives in form of hospital visits, being less conscious of one’s symptoms and most importantly, setting priorities on the livelihood. Thus mild to moderate symptoms (epiphora, mucopurulent discharge, painless swelling) which are not disastrous to one’s life, often got overlooked and it lead to significant epidemiological and clinical changes in cases of chronic dacryocystits.[5]
Materials and Methods
An observational study was designed from July 2020 to December 2020 in Regional Institute of Ophthalmology, Cuttack, Odisha, India. All the patients presenting with chronic dacryocystits were evaluated thoroughly in various epidemiological parameters such as age, gender, residence, occupation, comorbidities. The history and clinical features were noted, e.g. duration, number of attacks of acute dacryocystitis, epiphora, discharge, pain, swelling, previous surgery/procedure etc. After proper evaluation and conservative treatment, those patients were subjected for surgery (External Dacryocystorhinostomy/ Conjunctivo-dacryocystorhinostomy / Dacryocystectomy) and the surgical outcomes were followed-up upto 3 more months, i.e. March 2021.
Inclusion criteria
All cases diagnosed as chronic dacryocystitis.
ROPLAS test positive.
Lacrimal Passage Irrigation showing regurgitation from opposite/same puncta.
Both soft and hard stop on probing.
Acute on chronic presentation.
Exclusion criteria
Patients not giving consent to the study.
Patients lost to follow-up.
Secondary dacryocystitis due to nasal or bony pathology which requires treatment for the causative disease (tumours, wegener’s, rhinosporidiosis, tuberculosis).
Congenital dacryocystitis.
Results
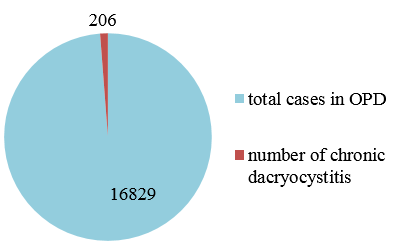
A subtotal of 206 patients were diagnosed with chronic dacryocystitis. Among them, 187 patients fulfilled all the inclusion and exclusion criteria’s. 8 patients were lost to follow-up, 4 did not give consent for further study and 7 had significant nasal or systemic disease which required intervention from the respective departments.
It was found that, during the study period, total attendance in the outpatient department of RIO, Cuttack was 16829. So, the prevalence was around 1.224%.
Among the 187 patients, 112 were female (59.9%) and 75 were male (40.1%). So, there is clear female preponderance.
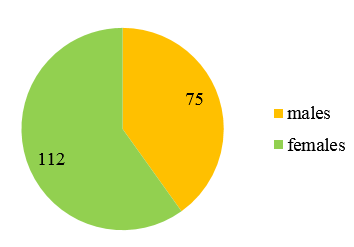
Chronic dacryocystitis was observed mostly in middle to old aged people with highest incidence in 51-60 years (30.5%). The percentage of cases in <20 years age group is 0.5%, however it is 1.6% in 21-30 years, 7.5% in 31-40 years, 24.6% in 41-50 years, 25.7% in 61-70 years and 9.6% in >70 years age group.
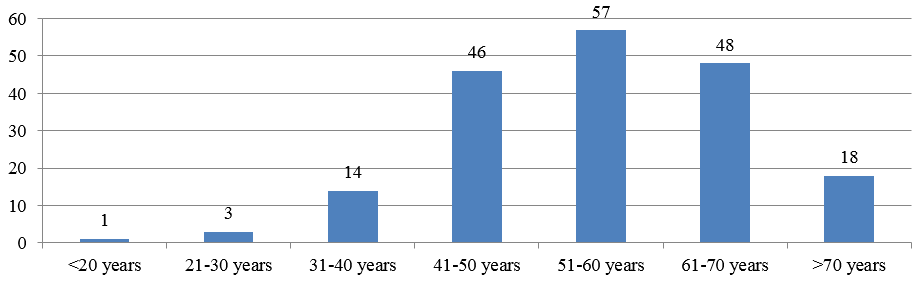
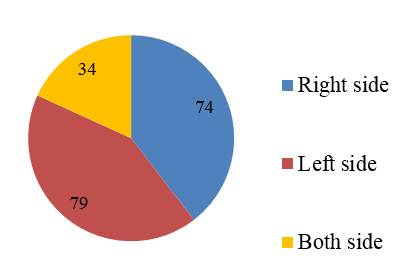
Chronic dacryocystitis is seen in right side in 74 cases (39.6%), left side in 79 cases (42.2%) and bilaterally in 34 cases (18.2%).
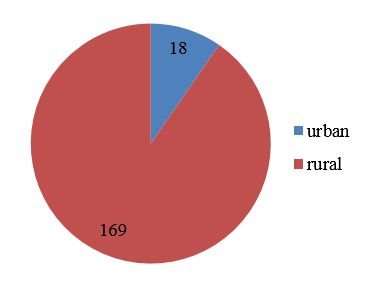
Most of the patients in the study group belonged to the rural population in Odisha 90.4% (169 patients), whereas 18 patients were from urban areas (9.6%).
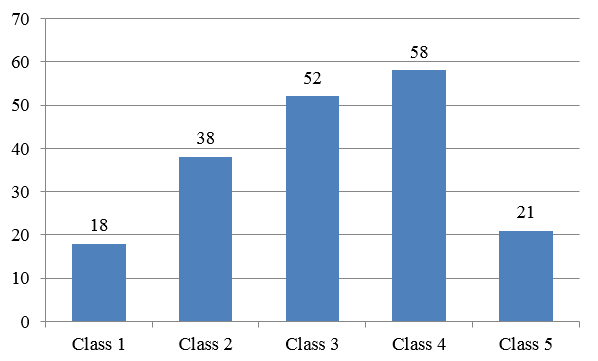
To determine the socio-economic status, we used the modified B.G. Prasad scale (2020). The study showed that, most of the patients belonged to social class 4(31%), followed by class 3(27.8%), class 2(20.3%), class 5(11.2%) and lastly class 1(9.6%).
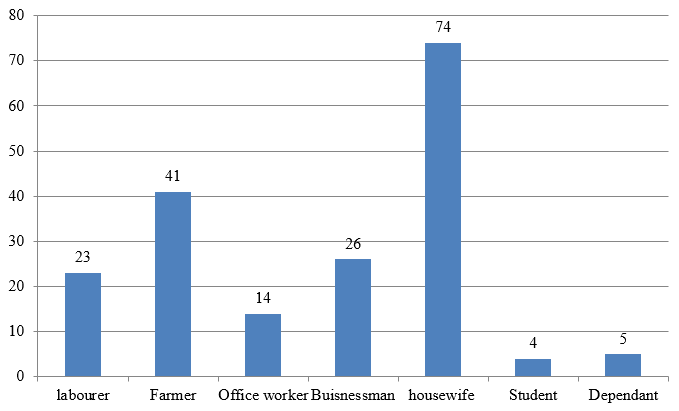
Analysis regarding the occupation of all these patients showed that most number of patients are housewives (39.6%) followed by farmers (21.9%). Businessmen (13.9%) and labourers (12.3%) also contributed significantly.
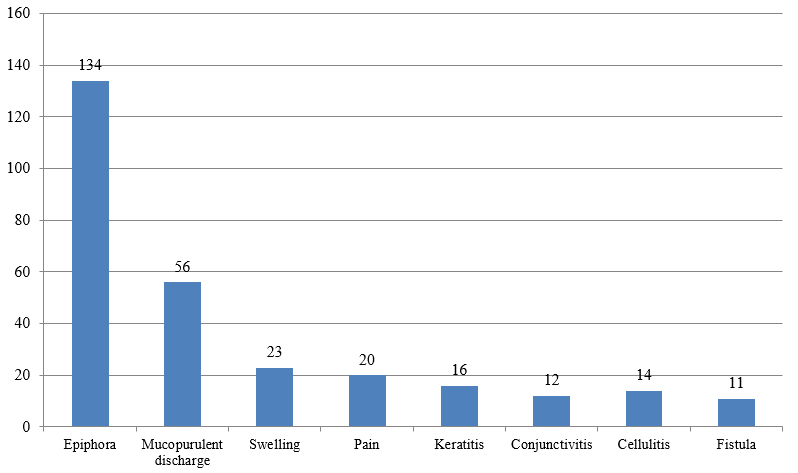
Regarding clinical features, 134 patients (71.6%) presented with epiphora which was the commonest symptom in the study group. Presence of mucopurulent discharge, pain, swelling in lacrimal sac area were present in 29.9%, 10.7%, 12.3% cases respectively. Other complications like conjunctivitis, keratitis, preseptal cellulitis, cutaneous fistula were seen in 6.4%, 8.4%, 7.5% and 5.9% cases respectively.
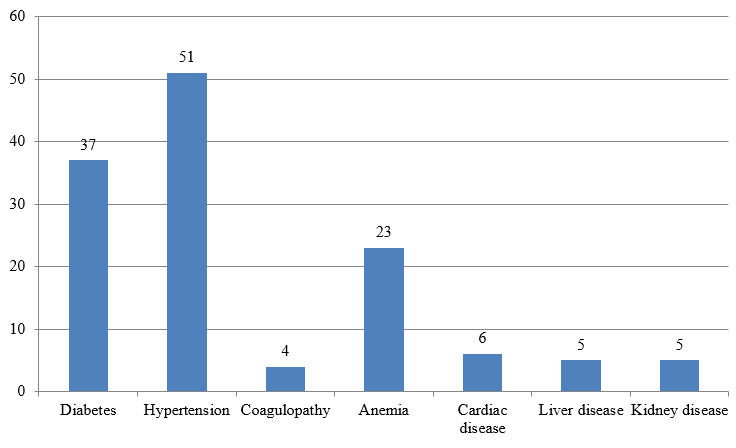
Enquiry is also made regarding any co-morbid condition which may affect the disease and surgical outcomes. History and laboratory work-up showed 37 patients having type 2 diabetes mellitus, 51 having hypertension, 4 with coagulation profile derangement, 23 with moderate to severe anemia (Hb<10gm/dl), 6 with cardiac disease, 5 with chronic liver disease, 5 with chronic kidney disease. 2 patients had history of DCR surgery in the same side.
After proper evaluation, pre-operative preparations and patient consent, total of 158 patients were taken up for surgery. DCY was done in 14 patients due to nasal/systemic pathology, old age being unfit for DCR. Among other 144 patients, 3 had canalicular block, so Conjunctivo-DCR was done with Lester Jones tube for those cases. Rest 141 patients had undergone external DCR under local anesthesia. After follow-up for at least 3 months, 20 patients of external DCR had reported reversal of previous symptoms, that is failure of surgery. So, the success rate for this surgery is 85.8% as per 3 months follow-up duration. However, no patient undergoing DCY or conjunctivo-DCR had reported any symptom signifying failure of surgery.
Discussions
In our study, higher incidence of disease was found in Females that is 112 (59.9%). This higher incidence in female may be attributed to narrow lumen of bony lacrimal canal and higher vascular congestive factors. It is comparable to a study carried out by Pawar and Patil[6], where incidence of Chronic dacryocystitis was seen in females in 56% of cases. Other comparable studies are Jacobs HG,[7] R. Dalgleish et al[8] (54%). Higher incidence of 61.6%, 67.86% and 84.6% were noted in Payal Katre et al,[9] Surendra P W et al[10] and Saxena R C et al[11] respectively.
We also found that the disease prevalence was highest in the age group of 51-60 years that was 30.5% followed by 25.7% in the age group of 61-70 years which is similar to Surendra P W et al[10] study. Jacobs HG[7] in his study found maximum incidence in age group of 40-55 years. While Saxena RC et al,[11] R Dalgleish et al[8] and Sarda et al[12] quoted a maximum age incidence in the 4th decade in their separate studies.Duke Elder S[13]stated that the disease preferentially affects adults over middle age being relatively rare in children and adolescents. The highest incidence quoted by him also was in the fourth decade of life.
In our study 42.2% had left sided obstruction, 39.6% had right side obstruction and 18.2% had bilateral obstruction. There is no significant laterality found. This is in accordance to the studies done by Reddy P S et al,[14] Jacobs HG,[7] Pandey R et al[15]Ramamani et al.[16]
The prevalence of Dacryocystitis is also very much related with socioeconomic status and its impact on living standard. and people belonging to class 4 & 3 were affected more, similar to Surendra P W et al[10] and Acharlu et al[17] in which they showed more prevalence in class 3 and 5. This can be attributed to poor hygienic conditions and low living standards. Presence of allergens such as household smoke, dust, pollen, agricultural pesticides may bethe causative factors, which has an important role in chronic sinus infections and chronic inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct. In our study, 90.4% were from rural population. The rural population of Odisha is 83.32%, so more predilection in rural community is anticipated.
The study showed that majority of the affected were housewives (39.6%) and farmers (21.9%), followed by small businessmen (13.9%) and wage labourers (12.9%) which showed that majority of the patients belonged to poor and low middle class families who lack in their cleanliness and hygiene. Outdoor exposure to irritant substances may also be an important factor in farmers and labourers. Chronic Dacryocystitis is less common among people of urban areas with middle class to rich class who can afford maximum hygienic measures. Surendra P W et al[10] reported most cases among daily labourers followed by farmers.
In our study, epiphora was the commonest presenting symptom in 134 patients (71.6%) followed by the symptom of mucopurulent discharge in 29.9% and swelling near the medial canthus in 12.3% cases. It correlates well with studies by Hartikainen J et al,[18] Reddy PS et al[14] which showed most common presentation as epiphora in 76% and 80% cases respectively. Zilelioglu G et al[19] reported the incidence of epiphora in 86% and discharge in 3% cases.
Complications like conjunctivitis, keratitis, preseptal cellulitis, cutaneous fistula were present in 6.4%, 8.4%, 7.5% and 5.9% cases respectively in our study, all of which are more as compared to previous studies. It may be related to the prolonged lockdown before the study period, for which rural patients could not attend any medical facility.
Hypertension (27.3%) was the commonest associates in the study group which is consistent with the Indian population (29.8%). 19.8% of our study group had type 2 Diabetes mellitus which is more than the double of Indian population (8.9%). Diabetes have definite role in delaying the normal healing process which attributes to the chronicity of the disease.
The success rate of external DCR was reported as 85.8% in this study. It is similar to the data shown by M. Alnawaiseh et al[20] and Badhu B et al[21] who showed success rate of 82.8% and 88.6% in their respective studies. Other literatures[22], [23], [24], [25], [26], [27] showed wide range of success rate (80%-95%).
.
Conclusion
Chronic Dacryocystitis, though a common problem of lacrimal drainage system and most commonly presenting only with epiphora, is much less recognized disease, specially in rural population and in lower socio-economic community, thus patients may present late with one or more complications. Form our descriptive study design, it was seen that chronic Dacryocystitis was more common in females and in age group 51-60 years. It was more prevalent in rural Odisha, in lower socio-economic strata. Mostly affected persons were housewives, followed by farmers, small businessmen and labourers. If presented late in healthcare facilities, complications like conjunctivitis, keratitis, preseptal cellulitis, lacrimal abscess, mucocele, cutaneous fistula may occur which is the current scenario in post-lockdown era. Maintaining all precautions and guidelines for COVID-19, we should not delay treating these patients with surgical measures. The disease may not look immediate sight-threatening but it has long term complications either with life-long annoying epiphora or some serious complications like keratitis, orbital cellulitis, sinusitis, even meningitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis and brain abscess. The surgical success rate (85.8%) however is not affected much in spite of all these factors related to late presentation. This might decrease if long term follow-up period is adopted.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflicts of Interest
All contributing authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- ZC. Post graduate Ophthalmology . . 2020;2:1389-91. [Google Scholar]
- Bowling B. Kanskii Textbook of ophthalmology. 8th Edn.. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- . American Academy of Ophthalmology. 8th Edn.. . [Google Scholar]
- Levine M, RA. Manual of Oculoplastic surgery. 5th Edn.. . [Google Scholar]
- Basak S. Essential ophthalmology. 5th Edn.. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar MD, Patil SN, KG. A new approach to stent dacryocystorhinostomy in cases with blockage of the lacrimal drainage system. Proceedings of the XXV International Congress of Ophthalmology. 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H. Symptomatic epiphora. Br J Opthl. 1959;43(7):415-9. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Dalgleish R. Idiopathic acquired lacrimal drainage obstruction. Br J Ophtholmol. 1967;51(7):463-8. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Katre P. Epidemiological study of dacryocystitis in rural population Panacea. J Med Sci. 2017;7(1):11-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wadgaonkar S, Patil P, Nikumbh D, Rathod S, Sawat C. Epidemiology of chronic dacryocystitis with special reference to socioeconomic status: A rural hospital study. Indian J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016;2(1):51-6. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Saxena R, Garg K. Scope of Dacryocystorhinostomy.. J India Ophthal Soc. 1969;17:55-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sarda R, Kulshrestha O, Mathur R. Dacryocystorhinostomy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1961;45(2):138-43. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Elders D, S. Disease of lacrimal passages; system of ophthalmology. . 1974;XIII part-II:675-724. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P, Reddy B. Dacryocystitis; Aclinico-pathological study. J Indian Med Assoc. 1955;1:413-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. Dacryocystorhinostomy and the superior-inferior flap technique. Indian J Ophthalmol. 1967;15:94-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dalai R, Rout R, Mohapatra S, Mohapatra S. A Study on Clinical Profile and Outcome of Chronic Dacryocystitis in Adults in a Tertiary Care Center, Paripex. Indian J Res. 2018;8(9). [Google Scholar]
- Acharlu P, Vijayalekshmi S. State of the Art Study on Epidemiology of Chronic Dacryocystitis in Rural Community. Int J Cur Res Rev . 2020;12(10):10-3. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Hartikainen J, Lehtonen O, Saari K. Bacteriology of lacrimal duct obstruction in adults. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997;81(1):37-40. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Zilelioglu G, Tekeli O, Ugurba SH. Results of endoscopic endo- nasal non laser dacryocystorhinostomy. Doc Ophthalmol. 2002;105(1):57-62. [Google Scholar]
- Alnawaiseh M, Mihailovic N, Wieneke A, Prokosch V, Rosentreter A, Merté R. Long-Term Outcomes of External Dacryocystorhinostomy in the Age of Transcanalicular Microendoscopic Techniques. J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:1-4. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Badhu B, Dulal S, Kumar S, Thakur S, Sood A, Das H. Epidemiology of Chronic Dacryocystitis and Success Rate of External Dacryocystorhinostomy in Nepal. Orbit. 2005;24(2):79-82. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Horix D, Struck HG. Long term patency rate of the external dacryocystorhinostomy. A retrospective study in the years 1991-2000 at the University Eye Hospital in Halle. Ophthalmologe. 2004;101(3):268-77. [Google Scholar]
- Huang J, Malek J, Chin D, Snidvongs K, Wilcsek G, Tumuluri K. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Outcomes for Endoscopic Versus External Dacryocystorhinostomy. Orbit. 2014;33(2):81-90. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Mäntynen J, Yoshitsugu M, Rautiainen M. Results of Dacryocystorhinostomy in 96 Patients. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 1997;117:187-9. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Shun-Shin G, Thurairajan G. External dacryocystorhinostomy---an end of an era?. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997;81(9):716-7. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Warren J, Seiff S, Kavanagh M. Long-Term Results of External Dacryocystorhinostomy. Ophthalmic Surg, Lasers Imaging Retina. 2005;36(6):446-50. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Saha R, Kumar P, Maurya R, Singh V, Singh M, Kumar R. Endoscopic V/s External Approach DCR: A comparative Analysis. Indian J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015;1(3):137-42. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Ghosal A, Chaudhury P, Kumar S, Khilar J, Rout N. Epidemiology, clinical profile, complications and treatment outcomes of chronic dacryocystitis in a tertiary care hospital in post lockdown era: An observational study [Internet]. IP Int J Ocul Oncol Oculoplasty. 2021 [cited 2025 Sep 18];7(2):151-156. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijooo.2021.030
APA
Ghosal, A., Chaudhury, P., Kumar, S., Khilar, J., Rout, N. (2021). Epidemiology, clinical profile, complications and treatment outcomes of chronic dacryocystitis in a tertiary care hospital in post lockdown era: An observational study. IP Int J Ocul Oncol Oculoplasty, 7(2), 151-156. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijooo.2021.030
MLA
Ghosal, Antarlin, Chaudhury, Pranati, Kumar, Siddharth, Khilar, Jyotish, Rout, Nirupama. "Epidemiology, clinical profile, complications and treatment outcomes of chronic dacryocystitis in a tertiary care hospital in post lockdown era: An observational study." IP Int J Ocul Oncol Oculoplasty, vol. 7, no. 2, 2021, pp. 151-156. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijooo.2021.030
Chicago
Ghosal, A., Chaudhury, P., Kumar, S., Khilar, J., Rout, N.. "Epidemiology, clinical profile, complications and treatment outcomes of chronic dacryocystitis in a tertiary care hospital in post lockdown era: An observational study." IP Int J Ocul Oncol Oculoplasty 7, no. 2 (2021): 151-156. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijooo.2021.030
